The Endocannabinoid System and How Cannabis Interacts with it

The Endocannabinoid System and How Cannabis Interacts with it
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) was discovered in the 1960s and 70s following research into cannabis effects on the body. The ECS is a complex system that's like a communications hub between the brain and essential body parts and functions. Despite extensive research, it's still not fully understood. Buts scientists have discovered it plays a vital role in our sleep, mood, appetite, memory, and reproduction functions. The ECS is always active in your body, regardless of whether you take cannabis or not.
How does the Endocannabinoid System Work?
There are three central components of the ECS: endocannabinoids (eCBs), cannabinoid receptors (CB receptors), and enzymes that synthesize and break down the eCBs.
Endocannabinoids (eCBs)
Like how the body's nervous system uses neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin as chemical messengers, the ECS uses endocannabinoids (eCBs) as its messengers which are produced throughout your body.
The two critical endocannabinoids identified so far are Anandamide (AEA), and
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
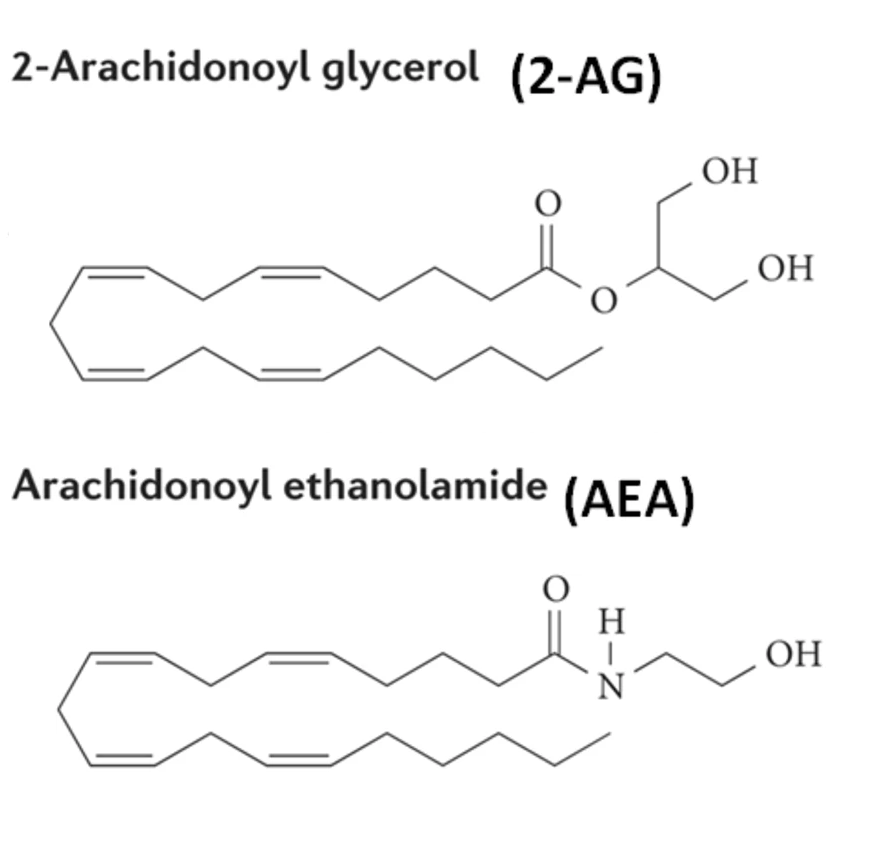
Anandamide (AEA)
Discovered in the 1990s, Anandamide, also known as N-arachidonoylethanolamine, is a fatty acid neurotransmitter. Anandamide was named from the Sanskrit word ananda, which means "bliss/joy." It is found throughout the ECS and is involved with memory, appetite, and pregnancy, to name but a few of its functions. The "runners high" experienced during intense workouts have been associate with it.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
Recent findings have linked 2-AD to emotional states as well as maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing seizures. Its been found in bovine and human milk. Its also linked to that satisfying feeling you experience after orgasm. Unlike Anandamide, 2-AG is found in relatively high levels in the central nervous system.
Cannabinoid Receptors (CB receptors)
These receptors are found all through your body. They sit on the surface of cells waiting to be triggered by the eCBs when these neurotransmitters bind to them.
There are two main CB receptors. CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors. Most cannabinoids can bind to both CB1 & CB2 receptors. This is the case for both endocannabinoids, 2-AG and AEA. However, this is not the case for CBD, which doesn't directly trigger the receptor. Rather change the receptor's ability to bind to cannabinoids. The results depend on which type of cells the CB receptors are on and what eCBs attach to them.
CB1 receptors are the most common receptors found in the central nervous system. They are essential for a healthy brain function. Depending on the area of the brain they are located, they can moderate mood (amygdala), memory (caudate nucleus/hippocampus), motor function (cerebellum), and your perception of pain. As you might have guessed, they are also responsible for the psychoactive properties of cannabis when they bind with THC. While they are most commonly found in the central nervous system, CB1 receptors are also found in other parts of the body but at lower concentrations. They play a part in hormone production, pregnancy, digestion, and cardiovascular health.
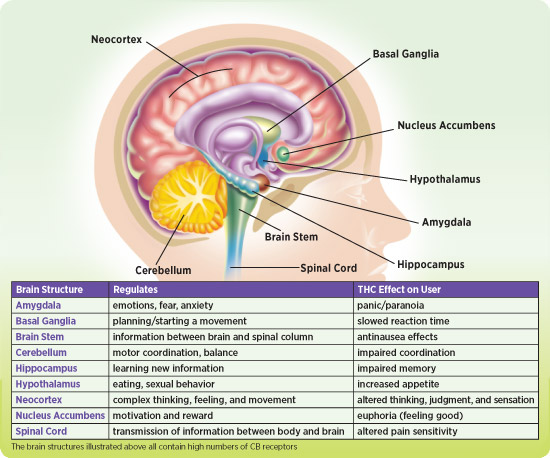
Image credit: headsup.scholastic.com
CB2 Receptors are most common in your body's peripheral nervous system, especially the immune system. They help with inflammation and immune responses to pathogens. If you use cannabis to treat asthma, allergies, arthritis, or autoimmune disorders, then it's your CB2 receptors, you should be thanking.
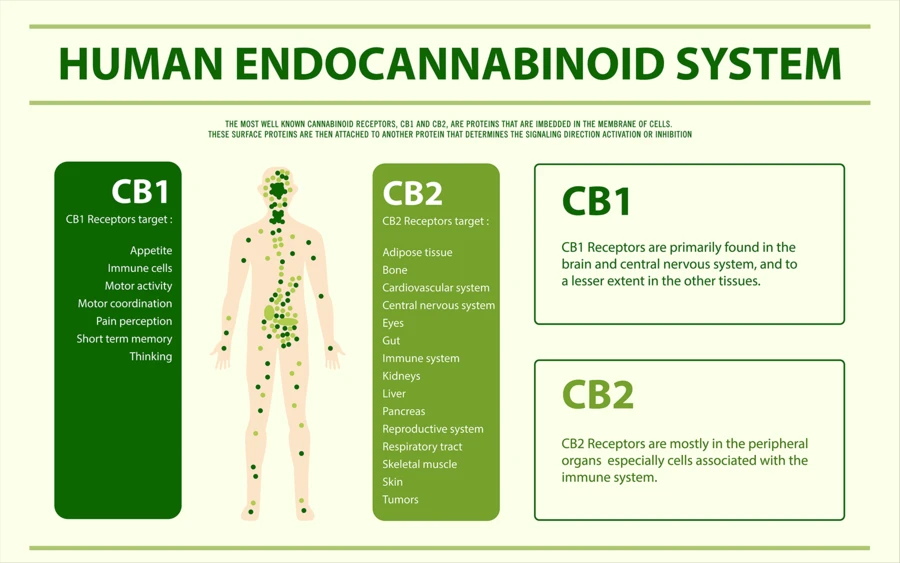
Image credit: cbdpillow.com
Enzymes
If endocannabinoids (eCBs) are the messengers, the enzymes are the system that creates the messages; you can think of them as the administration system of the ECS, telling the messengers where to go and when they are needed and in what quantities. eCBs are lipid-based neurotransmitters, so they are synthesized from fats. The body uses enzymes that work together, turning the fat into A2G and AEA. So a healthy diet with sufficient intake of good fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6 will help your body have the resource to create eCBs.
After the 2-AG and AEA eCBs have delivered their message and done their job, the body needs a way to turn them off; otherwise, they go on stimulating the ECS forever. Transport proteins will move the eCBs to storage sites in the body where enzymes can then degrade and recycle them.
Two of the most studied enzymes for degrading and breaking down the eCBs are MAGL and FAAH. MAGL breaks down 2-AG, and FAAH does the same for AEA.
An interesting genetic variation in around 20% of adults means their FAAH enzymes are impaired. The result is an increased level of AEA, which results in these people being less anxious. CBD also inhibits these enzymes so it can help the body's levels of feel-good factor AEA and 2-AG.
Promoting Good ECS Health
Each eCB can bind with many receptors, and each receptor can bind to many eCBs creating a tangled web of links and messages flying around the body. Many other molecules interfere or facilitate this binding, and because of this intricate detail, scientists are still trying to unweave this web and understand it fully. There are thousands of papers and studies which have helped bring us closer to understanding the ECS. We have learned that the ECS can be easily thrown out of balance by the hectic pace of our modern life's. Stress levels, exercise, and diet all play a role. If you're trying to balance your ECS there are over 100 different phytocannabinoids such as THC, THCa, CBD, CBDa, CBN, etc., which can all have a slightly different effect on the CB receptors throughout your body. As our understanding of the ECS expands, we will develop ways to target specific aspects of your immune and nervous system without activating the whole system.
You may also like to learn all about CBD concentrates or check out our article on the history of the bong.





